 |
| Trypophobia is a fear or disgust of closely packed holes. People who suffer have a feel of queasy when looking at surfaces that have small holes.gathered close together -- Image from CNN.com |
Trypophobia -Overview
The term, Trypophobia, which was first heard in 2005 and gained popularity on social media, has quickly become buzzword online for the adverse reactions some people experience when looking at an image of closely packed holes, such as honeycomb, lotus pods,or sponges. Some people have reported anxiety upon viewing such images, but the phobia is not yet recognized as a medical diagnosis. The word is derived from the Greek trýpa, meaning "hole" and phóbos, meaning "fear".
What is Trypophobia ?
Trypophobia is a fear or disgust of closely packed holes. People who suffer have a feel of queasy when looking at surfaces that have small holes.gathered close together. Not much is known but some common triggers are reported from them who suffers, for example
- Honey Comb
- Lotus Seed pods
- Coral
- Strawberry
- Bubbles
- Condensations
- Aluminum Metal Foam
- Pomegranate
- Cantaloupes
- A cluster of eyes
- Aerated Chocolate
- Stacked Industrial Pipes viewed end on
Symptoms
Despite their innocuous nature, images of above triggers can induce a variety of symptoms including cognitive changes that reflect anxiety, bodily symptoms that are skin related (such as itchiness, goose-bumps etc.) and physiological changes ( such as nausea, breathing trouble, irregular heart and pulse beat etc.).
Mathematical Properties that can relate the Symptoms
It appears that it is the configuration that holds the key to the
emotion that the images induce. Individuals who do not profess
trypophobia still find trypophobic images aversive, although they do not
experience the emotion. They do so because the configuration gives the
image mathematical properties that are shared by most images that cause
visual discomfort, eyestrain or headache.
Images with mathematical properties cannot be processed by the brain efficiently and so brain require more oxygenation. The discomfort occurs while looking the images with mathematical properties therefore normally people avoid such images. Trypophobic images among those that are intrinsically uncomfortable to look at.
Images of contaminants such as mould and skin diseases can provoke disgust in most people not just those with trypophobia. This disgust is probably an evolutionary mechanism that promotes avoidance and has survival value.
Images of mould and skin lesions have mathematical properties similar to those of images that are trypophobic. They also may induce a large oxygenation of the brain in addition to being generally uncomfortable. Perhaps discomfort is a useful mechanism not only for avoiding excessive oxygenation, but also for rapidly avoiding objects that provide a threat in terms of contamination. It may be that in people with trypophobia, the mechanism is overworking.
More from Disgust
New research by Emory University in Atlanta Georgia which was published in the open-access journal Peerj.com on 4th January 2018, shows that it may not be phobia at all. While phobias are triggered by the emotion of fear. It concludes that trypophobia is more likely driven by disgust instead..
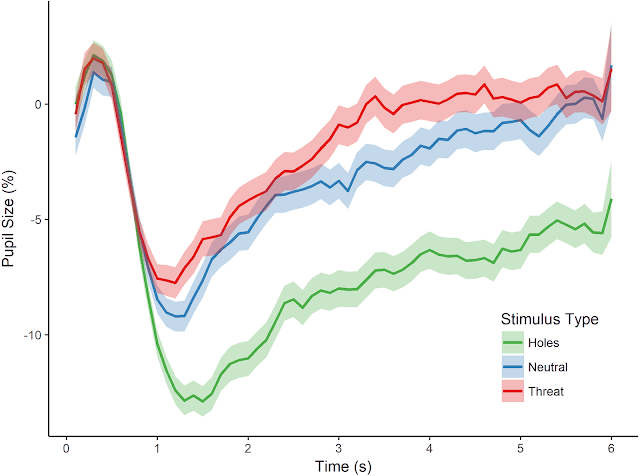
In the study, they used pupillometry to differentiate fear and disgust reactions to images of holes. Pupillometry provides a measure of pupil size, which is regulated by dilator and sphincter muscles. Crucially, these two muscles are differentially influenced by activity in sympathetic and parasympathetic branches of the nervous system. There is much evidence for a relation between fear and activation of the sympathetic nervous system, known for triggering a “fight-or-flight” response.
A fear response includes an increase in overall cardiovascular function, namely heart rate acceleration and a response in the dilator muscles, prompting pupil dilation (i.e., larger pupil size). By contrast, disgust is largely characterized by a response of the parasympathetic nervous system, known for “rest-and-digest” functions. These functions include slowing of cardiovascular functions, specifically decreased heart rate and a response in the sphincter muscles, prompting pupillary constriction (i.e., smaller pupil size).
Experiment 1 was conducted among 41 undergraduate students of average age of 19.84 years and out of them 30 are female.
Experiment 2 was participated by 44 other students ,average age of 19.60 years among them 30 are female. In the result, sample of 2 participants were removed for technical reason.
The research suggests that smaller pupil size report feelings of disgust, rather than fear, which is characterized by larger pupil size. That is because a fearful response involves an increase in cardiovascular functions, such as heart-rate acceleration, prompting pupil dilation as a result of perceived danger.
On the other hand disgust is associated with the opposite- the slowing of heart rate as a result , smaller pupil size- in response to perceived contamination.
The American Psychiatric Association does not recognize Trypophobia as an official phobia. Their Diagnostic and Statistical Manual (DSM-5) states
More research is needed to understand the full scope of trypophobia and the causes of the condition
Risk Factors
Not much is known as the risk factor linked to trypophobia but people across the globe have reported major depressive disorder and generalized anxiety disorder. There are two different study conducted in 2016 and 2017 have confirmed relation of these disorders with trypophobia,
(Ref NCBI) and perj.com -Fear of eyes: triadic relation among social anxiety, trypophobia, and discomfort for eye cluster
Diagnosis and Treatment
As Trypophobia is not yet officially recognized phobia therefore Doctors are more likely go with symptomatic treatment with consultation patient's medical, psychiatric and social history.
However for phobia there are different ways that can be treated. The most effective form of treatment is known as exposure therapy. It is a type of psychotherapy that focuses changing some one's response to the object or situation that causing discomfort.
Another popular treatment for a phobia is cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT). CBT combines exposure therapy with other techniques to help for managing anxiety and keeping thoughts becoming overwhelming.
Apart from these there are some ways to control phobia that includes
- Medication with proper guidance from a medical practitioner
- General talk therapy with a counselor or a psychiatrist
- Relaxation techniques such as yoga , deep breathing
- Physical activities and exercise to manage anxiety
- Mindful breathing, observation, listening etc to help cope with stress.
It is proven that by changing behavioral pattern and little modification of life style anybody can face boldly anything like phobia. Such as
- getting enough rest
- eating a healthy and balanced diet
- avoiding caffeine and other similar substances
- reaching out to friends, family and other support group to connect with other people managing the same issues
- face fearful situations head on as often boldly as it comes
Final Thought
Recently Trypophobia received significant media attention and American Horror Story featured a trypophobic character and trypophobic advertisements promoting the story line. some people were disturbed by the imagery and criticized the show for insensitivity towards sufferers of trypophobia. However it is obvious that by the increased media attention people become aware of the situation and encourage more research on the matter.














No comments:
Post a Comment